Taxable vs. Non-Taxable Crypto Transactions: A Guide for Smart…
As cryptocurrency gains popularity as a global investment niche, it has drawn attention from both investors and tax authorities. Understanding crypto tax implications is important for investors and traders alike. One of the most confusing aspects for crypto users is identifying which transactions are taxable and which are not. Whether you are based in the U.S., India, or elsewhere, distinguishing between taxable and non-taxable crypto transactions is essential for staying compliant and optimizing your financial strategy.
At Blockstats, we break it down in simple terms to help you easily understand which crypto transactions are taxable, which are not, and how you can confidently stay ahead of your tax obligations.
What makes a Crypto Transaction Taxable?
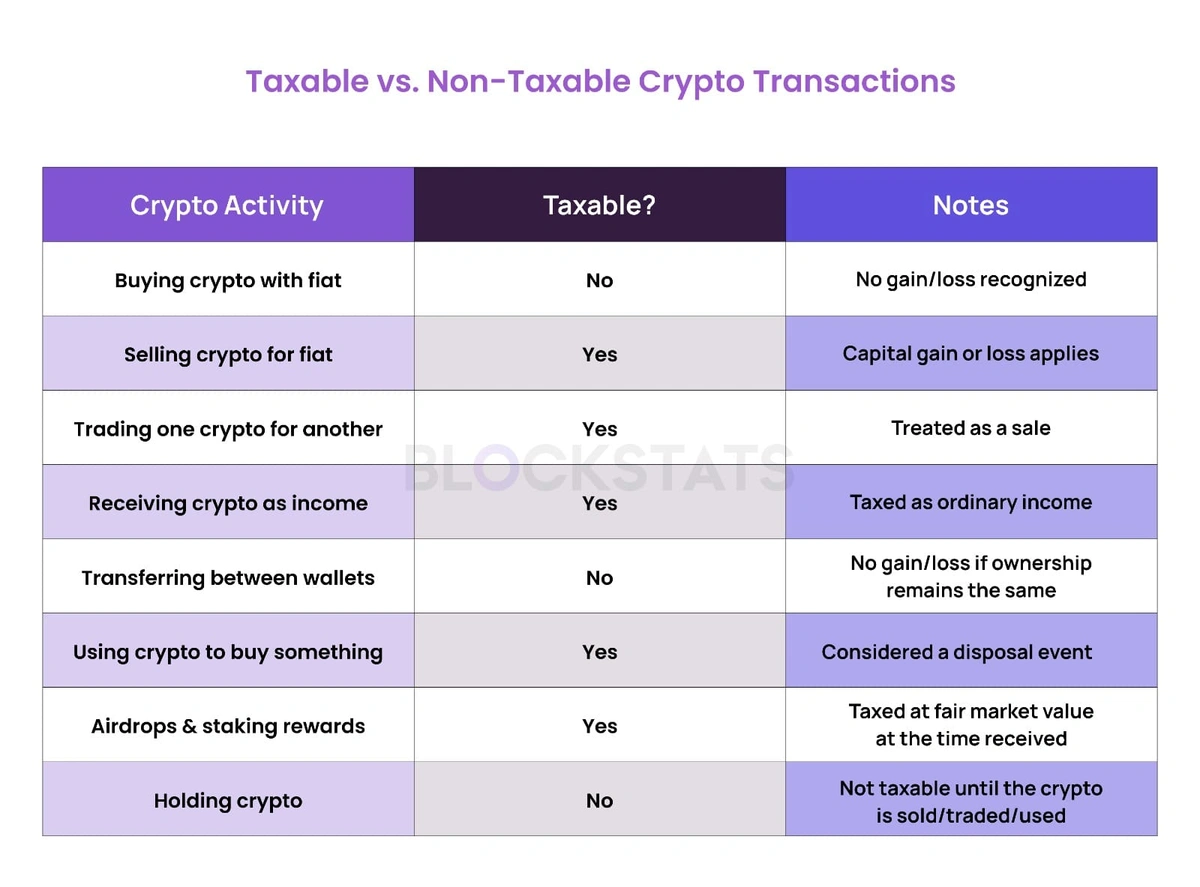
Taxable events in the crypto world typically involve scenarios where there is a realization of income or capital gains. Here are common taxable scenarios:
-
Selling Cryptocurrency for Fiat Currency: Converting crypto assets like Bitcoin or Ethereum into traditional currencies (e.g., USD, INR, GBP) often results in capital gains or losses, which are considered a taxable event.
-
Trading One Cryptocurrency for Another: Exchanging one crypto asset for another (e.g., Bitcoin for Ethereum) is considered a disposal of the original asset and will trigger capital gains tax.
-
Using Cryptocurrency to Purchase Goods or Services: Buying a car or even a cup of coffee with crypto? Spending crypto on products or services is treated as a sale of the asset, potentially leading to taxable gains.
-
Receiving Cryptocurrency as Income: Earning crypto through mining, staking rewards, airdrops, or as payment for services is typically considered ordinary income and is taxable at the fair market value at the time of receipt.
-
Gifting Cryptocurrency: In some jurisdictions, gifting crypto can be a taxable event, especially if the gift exceeds certain thresholds or if it is not to a spouse or civil partner.
Want to know your estimated tax? Checkout our crypto tax calculator.
What are Non-Taxable Crypto Transactions?
Not all crypto activities result in tax liabilities. Non-taxable events generally include:
-
Holding Cryptocurrency: Simply holding onto your crypto assets without selling, trading, or spending them does not trigger a taxable event.
-
Transferring Between Personal Wallets: Moving crypto between wallets you own is not considered a taxable event, as there is no change in ownership.
-
Donating to Registered Charities: In some countries, donating crypto to recognized charitable organizations will not be considered a taxable event, and it also provides tax deductions.
-
Gifting Below Thresholds: Small gifts of crypto that fall below certain value thresholds will not be subject to taxation, depending on local laws.
Taxable vs. Non-Taxable Crypto Transactions: Quick Comparison Table
Check your crypto gains with our free crypto profit calculator
Navigating Crypto Taxation in the U.S. and India
United States:
-
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) treats cryptocurrencies as property.
-
Capital gains tax applies to profits from selling or trading crypto.
-
Crypto received as income (e.g., mining, staking) is taxed as ordinary income.
-
Detailed record-keeping is essential for accurate reporting.
Read more: Calculate crypto taxes in 2026 step-by-step U.S. Guide
India:
-
The Income Tax Department classifies cryptocurrencies under the category of Virtual Digital Assets (VDAs).
-
Gains from VDAs are taxed at a fixed rate of 30%, with no deductions allowed.
-
A 1% Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) is levied on certain transactions.
-
Losses from VDAs cannot be used to offset income from other sources or carried forward.
Best Practices for Crypto Tax Compliance
Think of crypto tax compliance as a year-round process, not just an annual obligation. By staying organized with transaction records and understanding regional regulations, you can minimize errors and avoid penalties. Proactive planning today saves costly corrections tomorrow.
-
Maintain Detailed Records: Document every transaction, including dates, amounts, counterparties, and the purpose of the transaction.
-
Use Reliable Crypto Tax Software: Leverage tools that can import your transaction history and calculate tax liabilities accurately.
-
Stay Updated on Tax Laws: Crypto taxation is evolving; regularly consult official tax authority guidelines or a tax professional.
-
Report Accurately and Timely: Ensure all taxable events are reported in your annual tax filings to avoid penalties.
Turn Crypto Tax Complexity into Clarity with Blockstats
Understanding the distinction between taxable and non-taxable crypto transactions is important for effective financial planning and compliance. As regulations continue to grow, staying informed and proactive in your tax obligations will safeguard your investments and peace of mind.
Handling crypto taxes can be straightforward and stress-free. Blockstats offers a comprehensive platform that seamlessly tracks your crypto transactions, categorizes taxable events, and generates ready-to-file tax reports tailored to your jurisdiction. Stay compliant and make informed decisions with Blockstats—your trusted partner in crypto portfolio management and tax reporting.
What are you waiting for, start your free Blockstats account now.